Introduction to cloud computing 101
Cloud Computing is the demand delivery of computing services over the internet via Servers, Storage, databases, networking, software, and more.
Contents
- 1 TYPES OF CLOUD SERVICES:
- 2 CLOUD CHARACTERISTICS:
- 3 Types of Clouds in Cloud Computing:
- 4 Cloud Deployments in Cloud Computing:
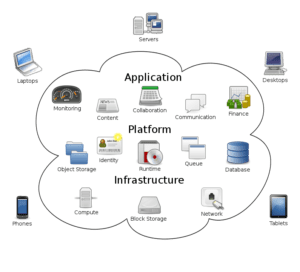
TYPES OF CLOUD SERVICES:
- Software as services
- Platform as services
- Infrastructure as services
SOFTWARE AS A SERVICES:
Software as a service refers to a software distribution model where applications are hosted by a third-party provider and made available to customers over the Internet.
Examples: Salesforce
PLATFORM AS A SERVICES:
Platform as a service is a cloud computing model that provides a platform allowing customers to develop run and manage applications.
Example : The Salesforce platform offers their enables developers to build and deploy custom applications
INFRASTRUCTURE AS A SERVICES:
Infrastructure as a Service is a cloud computing model that provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. In IaaS, customers rent virtualized servers, storage, networking, and other infrastructure components from a cloud provider on a pay-as-you-go basis
Example: Amazon Web Services
CLOUD CHARACTERISTICS:
Agility:
- Improves user’s ability to re-design technological infrastructure resources as per requirement.
Application programming interface (API):
- Cloud services/hardware should be programmable to customize and utilize the cloud resources.
Device and location independence:
- Enable cloud user to access systems using a web browser regardless of their location or what device they are using ( PC, mobile, Phone, PDA, Tablet, etc.). Many a time off-site, and on-site models and accessed via the internet so that users can connect from anywhere.
Multitenancy:
- Where a single instance of the software runs on a server, serving multiple client organizations.
Centralization:
- Centralization of infrastructure and data application hosting make it efficient not only for delivery but also for maintenance.
Reliability:
- Delivery of data to the intended cloud recipient through reliable and secure protocols only.
Scalability:
- All the cloud resources should be scalable and measured not only on performance but also on usage, efficiency and on different measuring and quality parameters.
Elasticity:
- Dynamic on demand provisioning of cloud resources so that in case of increase of demand, the cloud resources should be elastic as expandable to accommodate all request without any delay or loss.
Performance:
- Cloud resources should be peak performance oriented to serve all received request with efficiency.
Cost:
- Cloud deliver model should be available at the lowest of price incurring saving for the organizations
Security:
- Centralization of data increased security focused resources implementing different security parameters and policies to make secure organization data.
Maintenance;
- Cloud computing applications should be easier to Install, Maintain from user friendly administration panel.
Types of Clouds in Cloud Computing:
Cloud computing has 4 types
- Private Cloud
- Public Cloud
- Community Cloud
- Hybrid Cloud
Private Cloud:
Private cloud computing resources such as server storage and networking infrastructure are provisioned and maintained for the exclusive use the organization.
A private cloud provides a higher degree of control, security, and customization.
Public Cloud:
Public cloud where computing environment resources, such as servers, storage, and networking infrastructure is owned and operated by a third-party cloud services
Community Cloud
Community cloud, these organizations collaborate to deploy, manage, and utilize shared computing resources provided by a third-party cloud service provider.
Hybrid cloud
Hybrid cloud, organizations can leverage the scalability and cost-effectiveness of public cloud services while retaining control over sensitive data and critical applications within their private cloud infrastructure.
Cloud Deployments in Cloud Computing:
- Network dependency.
- Subscribers still need IT skills.
- Risk for multi-tenancy.
- Data import/export and performance limitations
- Workload locations
Network dependency:
Organizations need a stable and high-speed internet connection to ensure seamless access to their cloud resources. Any disruptions or latency in the network can affect the performance and availability of cloud-based applications and services.
Subscribers still need IT skills.
Despite the ease of use and automation provided by cloud service providers, subscribers still require a certain level of IT skills and expertise to effectively manage and configure their cloud environments. Tasks such as resource provisioning, security configuration, and troubleshooting may necessitate technical knowledge and experience.
Risk for multi-tenancy:
Multi-tenancy is a characteristic of cloud computing where multiple users or organizations share the same physical infrastructure and resources. While multi-tenancy enables cost savings and resource efficiency, it also poses risks such as potential security vulnerabilities or performance degradation due to resource contention among tenants.
Data import/export and performance limitations:
Transferring large volumes of data into or out of the cloud can be challenging due to bandwidth limitations and potential costs associated with data transfer. Additionally, the performance of cloud-based applications and services may be impacted by factors such as geographic distance between users and data centres, as well as resource allocation and congestion within the cloud provider’s network.
Workload locations:
Cloud computing offers flexibility in deploying workloads across different geographic regions and data centres. However, the location of data and applications can have implications for factors such as data sovereignty, compliance with regulatory requirements, and latency-sensitive applications. Organizations must consider these factors when determining the optimal location for hosting their workloads in the cloud.
Learn more about cloud computing check out here
In the next topic discuss What is CRM
Who is the father of cloud computing?
Joseph Carl Robnett Licklider.
What are the three main service models in cloud computing?
The three main service models in cloud computing are Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
What is the difference between public, private, and hybrid clouds?
Public clouds are hosted and managed by third-party providers, private clouds are dedicated to a single organization and managed either internally or by a third party, while hybrid clouds combine elements of both public and private clouds.
What are cloud computing examples?
Emails, calendars, Skype, and WhatsApp
What are the key benefits of cloud computing?
Some key benefits of cloud computing include cost savings, scalability, flexibility, accessibility, and improved reliability and security compared to traditional on-premises IT infrastructure.

3 thoughts on “Introduction to cloud computing 101”